Metastatic Melanoma
What is metastatic melanoma?
Metastatic melanoma, also referred to as stage 4 melanoma, occurs when cancer spreads beyond the tumor into other parts of the body. Melanoma is a rare form of skin cancer that develops in the melanocytes, which are responsible for the production of melanin.
What are the symptoms of metastatic melanoma?
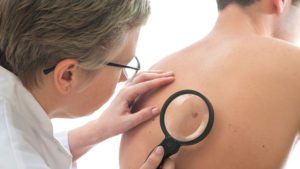
Before melanoma has spread, it will appear in the form of an unusual mole on the skin. These moles are asymmetric, discolored, larger in size, and have uneven borders.
Once the cancer has metastasized, symptoms will change depending on which parts of the body are impacted. Symptoms may include weight loss, hardened lumps under the skin, headaches, fatigue, weakness or numbness in the extremities, swollen or painful lymph nodes, enlarged liver, loss of appetite, difficulty breathing, cough, bone pain, broken bones, and seizures. Not every patient will experience every symptom, as they are dependent on the location and spread of the cancer.
What causes metastatic melanoma?
Exposure to UV light, whether that is through the sun or tanning beds, causes melanoma. Metastatic melanoma can then occur when a patient is not diagnosed or does not receive treatment.
Risk factors also exist for this cancer, including fair skin, a family history of melanoma, frequent exposure to UV light, a large number of moles, and older age.
How is metastatic melanoma diagnosed?
The first step in diagnosis is typically noticing an irregular mole and having it inspected by a dermatologist. A biopsy of the mole will be performed; if it shows melanoma, then doctors will perform additional tests to assess the spread. They will use a sentinel node biopsy to see if cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. If it has, they will go on to use MRIs, PET scans, X-rays, CT scans, and blood tests.
What are the treatments for metastatic melanoma?
The first step in treatment is to remove the tumor and surrounding malignant cells. Lymph node dissection and interferon will follow, and other treatment options include chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radiation.
Where can I find out more about metastatic melanoma?
Metastatic Melanoma Articles
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma (ALM) Rates Higher in Southeast Asian Individuals than Other Asian Groups

AVS100 Earns Orphan Drug Designation for Advanced Melanoma

These Three Organizations Are Revolutionizing Rare Cancer Research

Relatlimab + Nivolumab Increase Survival in Metastatic Melanoma
-300x300.jpg)
Metastatic Melanoma was Untreatable but Two Drugs Have Changed the Landscape





